8 Best Tourniquets of 2023
Whether you are stocking your car with first aid supplies on the way to the gas station or hearing a gunshots over the radio, it’s important and essential to have the first aid kit with tourniquet in your EDC and start to train using it. Although the fact is that much controversy are around the tourniquets in the military community – some think they are dangerous to cause bacterial infection, they are actually the best shot at survival if used properly.
There are different types of tourniquets on the market that can be a little pricey and hard for you to choose from. No worries! The post is here to help you master the common sense of tourniquets and figure out the best tourniquets of 2023 on the market.
What Is a Tourniquet?
Tourniquet is a strip of cloth or a band of rubber tightly wrapped around the limb to stop bleeding. Modern tourniquets are made of polymer, nylon, and aluminum. Hook and Loop are used to keep the strap in place and buckles are to apply direct pressure.
The Most Common Types of Tourniquets
Dating back to 1674 when they were cobbled together with sticks and bandages by battlefield surgeons, tourniquets have actually been around for centuries in the world. Nowadays, modern tourniquets offer more compact and convenient types to control massive bleeding.
There are four types of tourniquets and most of them are windlass. Here is a list of their respective characteristics.
Windlass Tourniquets
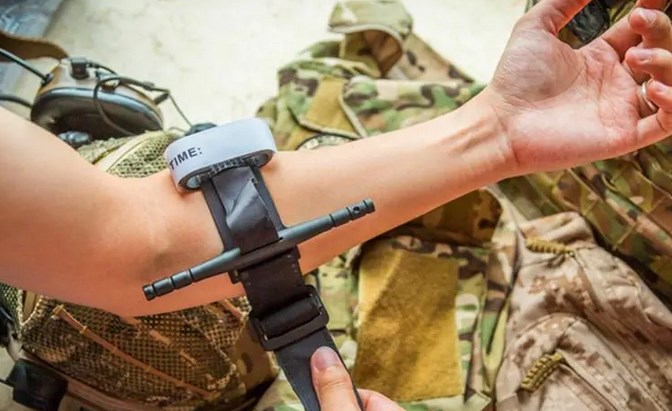

Windlass tourniquets consist of a loop strap that goes around the limb and a rod that turns to tighten the strap. If you need to make a temporary tourniquet, you will also want to use the windlass system because it is easy to make one and get the tourniquet tighter.
Elastic band
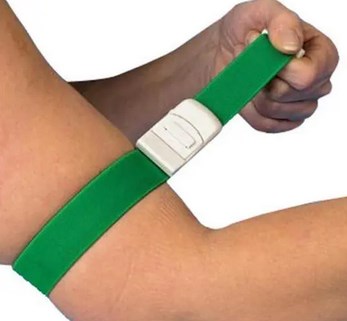
Made of long pieces of elastic material, elastic band allows you to wrap them around the limb several times and tuck in the end, which are easy to use but hard to get pressure on the bleeding wounds.
Ratchet Tourniquet

These tourniquets are similar with the ratcheting system used in ski boots. Since the skin or clothing may enter the ratcheting system to increase failure rate, they are not recommended.
Pneumatic Tourniquets
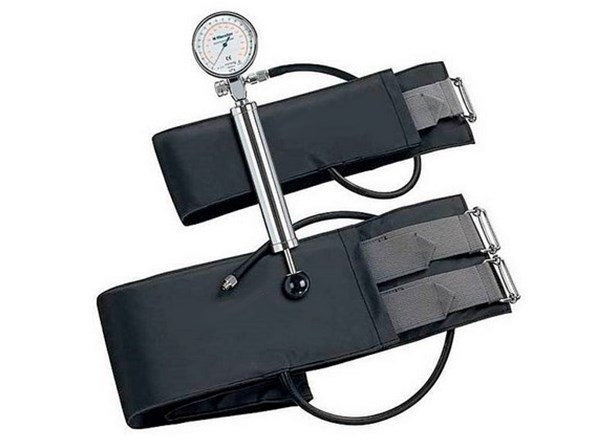

Pneumatic tourniquets use an inflatable bladder to create pressure and stop bleeding. Since it is more challenging for non-professionals to apply tourniquets, they are generally seen in hospitals. Thus, they are not recommended for most people.
How to Choose a Tourniquet?
- Consider the tourniquet material. Tourniquets must add huge pressure to collapse veins and arteries and be secured in place. Weak and flimsy material simply not power enough to exert the pressure.
- The best tourniquets must be intuitive to figure out and easy to use.
- An EDC tourniquet must be durable and reliable. Avoid cheap and counterfeit tourniquets and note that the windlass tourniquets may be easily snapped.
- Look for the tourniquet that meets the standards of the Committee on Tactical Combat Casualty Care (CoTCCC), part of the U.S. military’s Joint Trauma System, for use in combat situations.
Top 8 Tourniquets of 2023
1.Combat Application Tourniquet (C-A-T), Gen 7 by North American Rescue
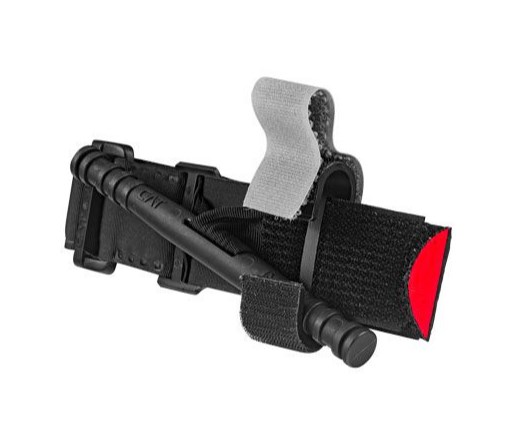

CAT tourniquet by North American Rescue is one of the most common version on the U.S market and one of the best recommended tourniquets by CoTCCC. Many imitators also make CAT tourniquets, but none of them ever shake the status of the authentic CAT. Specifically, it uses the open-loop design and adjustable hook & loop strap for quick one-hand operation. Relying on a reinforced polymer windlass with ridges and grooves, it provides firm grip in both wet and dry condition, The windlass is mounted to a stabilization plate for easier and safer application and the plastic windlass is used to tighten down skin where you need to stop bleeding.
The white Velcro can be used to mark the time when you apply tourniquet on your limbs. It is a necessary action to tell the medical professionals how long the tourniquet has been used. The windlass is locked to one of hooks on the side of the tourniquet and secured by white straps.
CAT won the bid to be Army’s standard-issued tourniquet in 2005 and has since become the most widely accepted gear for civilian, first responder, and law enforcement use.
So now you get a tourniquet, have you considered how to carry the tourniquet with you? It’s more convenient to put it in your own CAT tourniquet holder and carry it somewhere easily accessible than dig through your pocket.
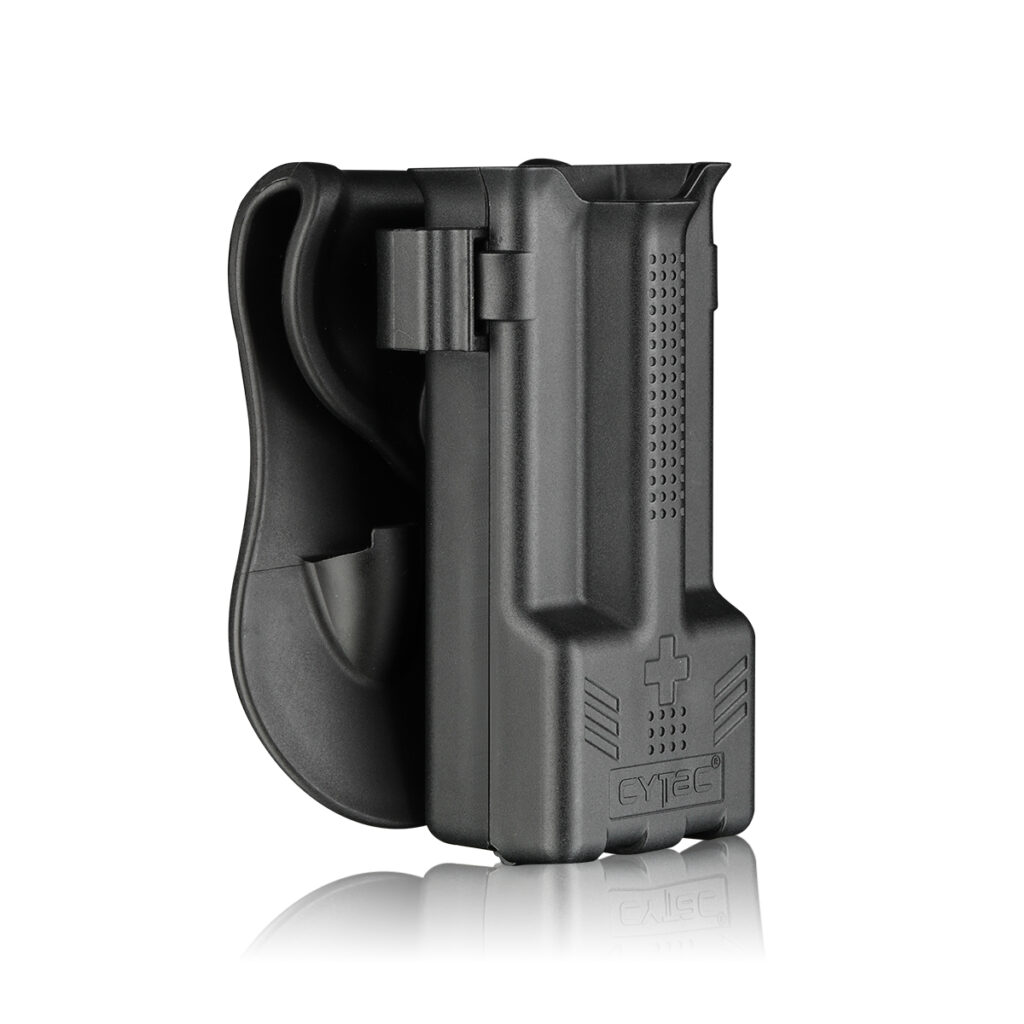 Cytac Vari-Fit Universal Tourniquet Holder (Item NO.: CY-THB-3) fits most tourniquets on the market, like C-A-T, SAM-XT, SOFTT-W-R, etc. As a duty belt tourniquet holder made of mil-spec durable polymer, this tourniquet holder can withstand most extreme tactical conditions and is a must to extend the time for survival in combat, field survival use, etc. The open-top design ensures a quick drawing in harsh conditions while the tension adjustment mechanism secures your tourniquet in place.
Cytac Vari-Fit Universal Tourniquet Holder (Item NO.: CY-THB-3) fits most tourniquets on the market, like C-A-T, SAM-XT, SOFTT-W-R, etc. As a duty belt tourniquet holder made of mil-spec durable polymer, this tourniquet holder can withstand most extreme tactical conditions and is a must to extend the time for survival in combat, field survival use, etc. The open-top design ensures a quick drawing in harsh conditions while the tension adjustment mechanism secures your tourniquet in place.
Now it is compatible with multiple different platforms with tooth gear, giving you much more flexibility and freedom to adjust the wearing cant in 360 degrees. These carrying platforms includes R-Quickads Clip, MOLLE, drop leg platform, paddle, low ride belt loop, should harness, etc.
For any further queries and concerns, please feel free to contact our sales team as always.
2.SOF Tourniquet Gen 4 (SOFTT-W) by Tactical Medical Solutions
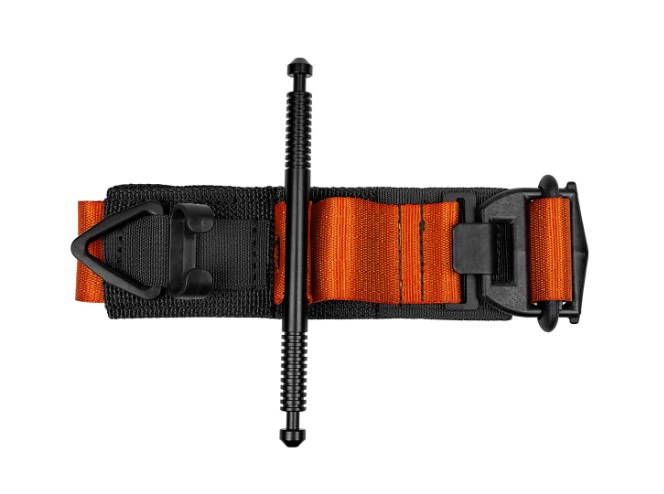

SOF tourniquet is well known and highly regarded in the Special Operations community. Featuring with an open-loop design and tough construction, it uses newly-added dual windlass clips to add pressure to where you want to stop bleeding. Instead of CAT’s plastic windlass, SOF’s metal and textured windlass is much easier and more compact to use with one hand or when your hands are slippery.
There are two types of SOF tourniquets. SOFTT offers only 1” standard width while upgraded SOFTT-W offers 1.5” width, which is also slightly expensive than the standard ones.
3.Tactical Mechanical Tourniquet (TMT) by Combat Medical Systems

As one of the newest tourniquet brand, TMT has quickly occupied the market and captured the hearts of CAT fans. As one of the recommended combat tourniquets approved by CoTCCC, TMT controls bleeding in an different approach by combining both CAT and SOF-T with hook and look and quick disconnect. Also, TMT adopts 2” strap to help stop bleeding in a more comfortable and effective way.
4.TX2 by RevMedX

Different from the traditional windlass tourniquets, TX2 by RevMedX controls bleeding with ratcheting mechanism. Like TXT introduced above, TX2 also uses 2” strap and has only occupied the market for years after acquiring the CoTCCC approval.
TX2 is hard for every day carry due to its size, and it requires a little practice for one-hand operation. Also, most tourniquets on the market are for one-time use and the windlass TQs start to degrade or fail after repeated use. Consequently, you have to buy two for training and rescue.
However, things are different with ratchet tourniquets. They are cheap and won’t wear and tear on the material after repeated use. Thus, getting one is enough for training and rescue.
5.SWAT-T by H&H Medical

SWAT-T looks too simple to be effective. With only a stretch band and being not approved by CoTCCC, most people don’t think it worth the time. In fact, it’s not approved by the US government since the method of securing is not as reliable as other TQs listed above. If applied correctly and checked every now and then until EMS arrives on scene, it won’t have any problems. However, it is fine for common users and even some Tier 1 level military units take this tourniquet with them in dangerous combat situations because of its comfortable user experience, compact size to carry in a pocket, and multi-function.
As for its multi-function, it’s the Leatherman of the trauma world. It works like a complete trauma kit rolled up with everything you need. Whether you want a press dressing or get fractured or dislocated, the SWAT-T can without doubt fulfill your demands.
6.Emergency & Military Tourniquet by Dekfi Medical Innovations
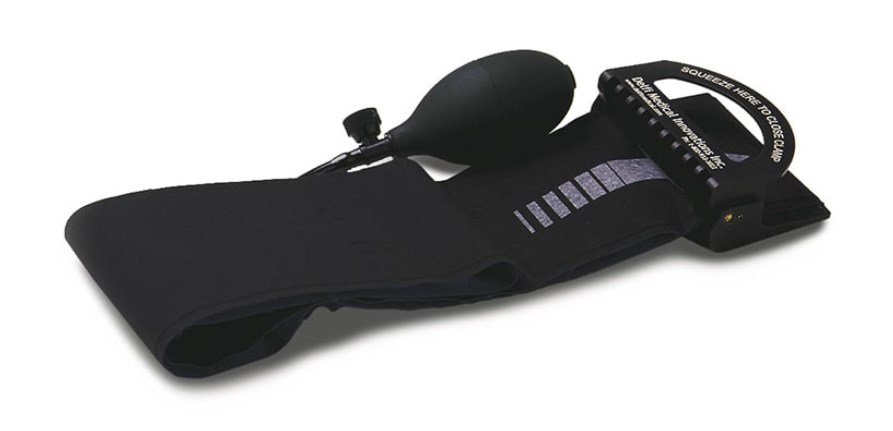

As a typical pneumatic tourniquet, Delfi EMT allows you to loop the cuff around the wounded limb and add circumferential pressure to block blood flow by squeezing the air bulb to inflate the central tube. It may be more comfortable than the windlass CAT-7 and SOFTT-W tourniquets since it is less likely to cause nerve damage.
7.Ratcheting Medical Tourniquet (RMT)
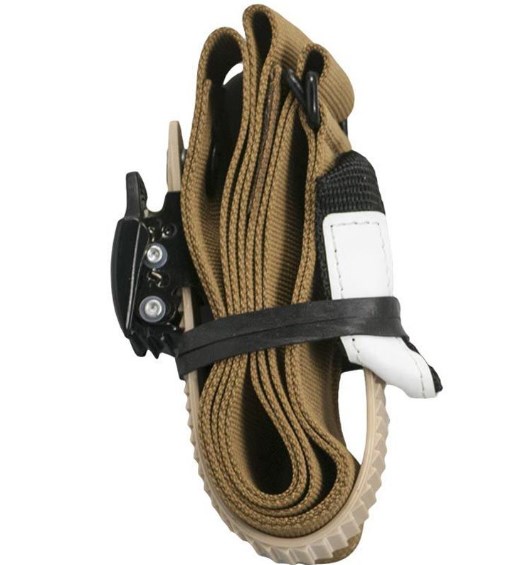

As its name shows, RMT means a series of tourniquets tightening the TQs with the ratcheting system. Although they are not as fast as windlass tourniquets and are more inclined to be jammed by clothing, they can close to a smaller diameter cuff, making them a great choice for children. Besides, RMT’s size is also small, you can carry it every day more easily.
8.SAM Extremity Tourniquet (SAM-XT)
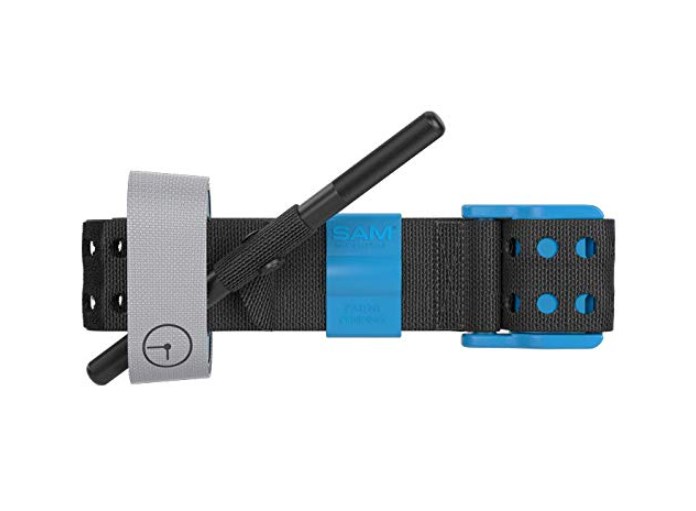

SAM-XT tourniquet is a relatively new type that doesn’t yet have the same reputation as CAT-7 or SOFTT-W, but it does make some upgrades on the appearance. There are some holes in the strap and it uses both Velcro and locking prongs to secure the strap, which removes slack and makes the tourniquet more effective.
How to Use a Tourniquet?
Applying a tourniquet correctly is an essential life-saving skill in life-threatening emergencies when a severe massive open wound is on your, a family member’s, or a complete stranger’s body. Cutting off the flow of blood must be completed as quickly as possible to avoid worse condition. Also note that using a tourniquet should be the last resort to use in life-threatening emergencies. If the tourniquet is not available, you should continue pressing the wound and elevate the injury.
Here are some tips for applying a tourniquet:
- Identify the source of blooding and locate the wound.
- Directly place the tourniquet above the wound on the side of the limb closest to the heart.
- Tighten the tourniquet with the tourniquet’s tightening mechanism to compress the wound. The tourniquet should be tightened until teh bleeding stops.
- Secure the tourniquet in place with a knot or clip to to keep it from slipping.
- Mark the time on the tourniquet or the victim’s skin to indicate how long a tourniquet has been used.
- Seek medical care: Transport the patient to a nearby hospital or call for local medical help. It’s necessary to get immediate medical help because leaving the tourniquet for too long can cause serious damages to the limb.
Other Must-have Bleed Stop Items
There are also other first aid supplies except for tourniquet you might use in case a tourniquet is not available, including coagulating bandage, gauze, medical adhesive tape, antibiotic ointment, cotton balls, etc. These items make you calm and give you a handy experience in emergencies.
Final Words
First aid is always an invaluable skill to address traumatic injuries in emergencies or prepare for unexpected situations in everyday life. There are different types of tourniquets on the market, but the procedure of applying a tourniquet is much the same. Moreover, the tourniquets approved by CoTCCC are reliable and recommended and other newer types are also worth a try. Keep exploring and stay prepared.

